In today’s fast-paced environment, measuring speed and distance accurately is imperative. Despite the presence of modern high-tech gadgets, one tool has stood the test of time in performing this vital task: the Tachymetric Scale.
This blog post delves into the fascinating world of tachymetric scales, providing an insightful guide into their purpose and operation.
Delving into their history and origins, this post sheds light on this often-underlooked but essential tool, exploring its application in diverse fields, from sports to aviation. Check out our awesome collection of tachymeter parts!
What is a Tachymetric Scale?
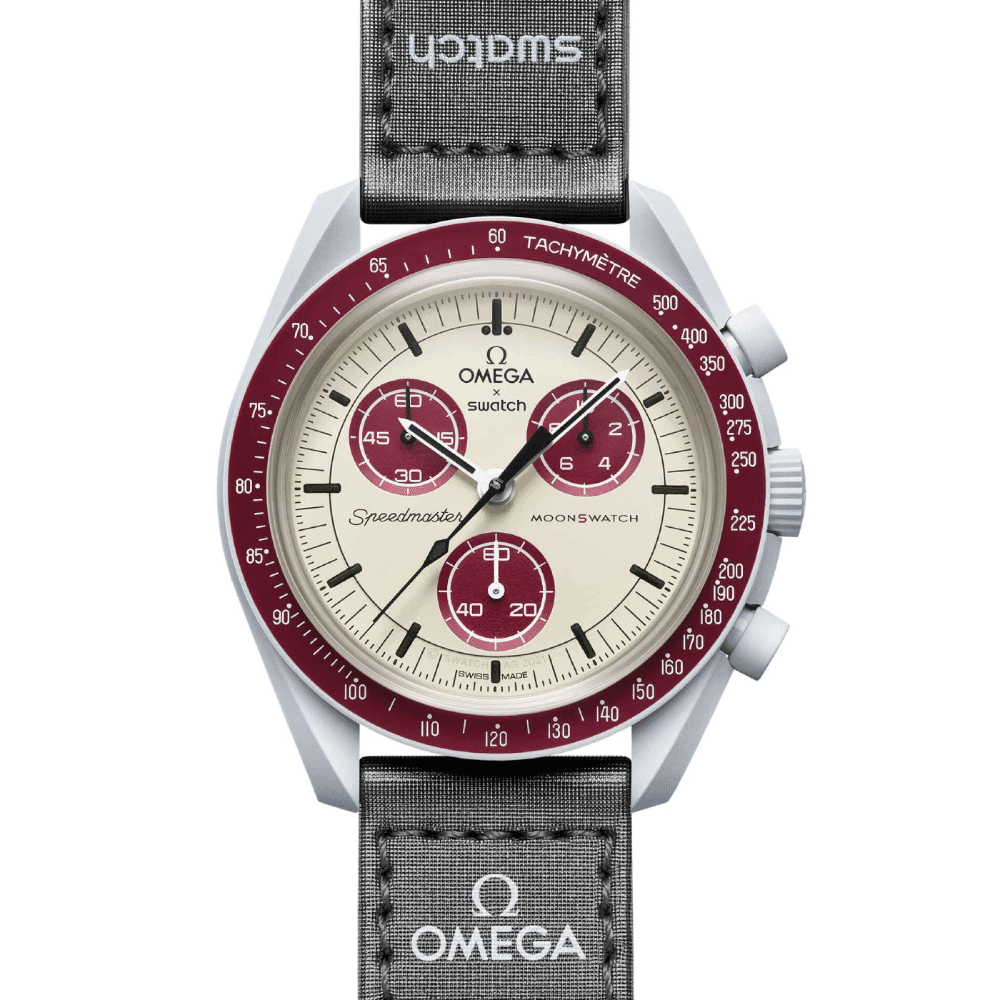
A tachymetric scale, also referred to simply as a tachymeter, is a form of measurement tool typically found on the rim of a chronograph watch. It is used to compute a speed based on travel time or measure distance based on speed. Derived from the Greek word tachymetron, it denotes “rapid measure.”
Purpose of a Tachymetric Scale
In essence, a tachymeter serves a quite straightforward but crucial function: it scales time into speed. In the realm of wearable timepieces, like wristwatches, a tachymeter is used for measuring speed (in kilometers or miles per hour) based on time traveled, or measuring distance traveled given a known speed.
This measurement tool plays a significant role in various industries where speed and time measurement are crucial.
Principle Behind a Tachymetric Scale
A tachymeter comprises an engraved numbered scale, typically located around a watch’s bezel or, in some designs, around the outer rim of the dial.
To understand effectively how a tachymeter works, it is essential to know one principle – the numbers inscribed on the tachymeter scale represent the speed at which an event occurs, within a set time frame.
For example, if you wished to determine your speed over a known distance of one mile or one kilometer, you would start your watch’s chronograph at the beginning of the route, and then stop it at the end.
The second hand’s position on the tachymeter scale shows your average speed over that distance.
Tachymeter: A Valuable Tool on Chronograph Watches
Despite its limitations, a tachymetric scale enhances the functionality, design, and appeal of a chronograph watch. With the ability to not only tell time but also measure speed and distance, they are particularly useful and appealing to athletes, pilots, and anyone who values the fusion of style and functionality in their timepieces. Check out other chronograph collections today!
Tachymetric Scale Across Fields
Tachymetric scales are not just useful for motorists to calculate their average speed, but these instruments have also found their place in various fields. For instance, in professional racing, a tachymeter proves to be advantageous, given its ability to measure mean speeds.
Apart from that, industries where time and speed play a vital role, such as aviation, marine navigation, and even space travel, have been utilizing the principles of a tachymeter. In manufacturing processes, it helps monitor production speed and efficiency.
In aviation, its use is more advanced. A tachymetric scale can infer the required time of flight for a specific distance, the distance that can be covered in a particular time, or the speed necessary to cover a specific distance in a given period.
Other Uses of a Tachymetric Scale
While time, speed, and distance measurement are the primary utilization of a tachymetric scale, it is also used to compute other units of measure. For example, one can measure the production rate in a factory – how many items are produced per hour.
As a practical and essential tool, the tachymetric scale is a vital instrument not just for watch enthusiasts, but also across multiple industries where calculations of speed, distance, and time are critical.
Despite the modern era’s digital advances, the accuracy and vintage charm of a traditional tachymeter continue to sustain its relevance and trustworthiness.
The Roots of the Tachymetric Scale
Today, the tachymetric scale is widely utilized for gauging speed based on time traveled or determining distance based on speed. This tool is particularly recognized for its incorporation in the bezel of chronograph watches.
Yet, its humble beginnings are rooted in the complex field of mathematics. The inception of the tachymetric scale can be traced back to the 19th century, thanks to the collaborative work of mathematicians, engineers, and watchmakers.
The term “tachymeter” originates from the fusion of two Greek words, “tachos” translating to “speed”, and “metron” which implies “measure”.
It was first christened by Benjamin Louis Francœur, a French mathematician and astronomer in 1809. Initially, the tachymeter’s role was within the industry, particularly in assessing machine speeds.
The Evolution and Broad Application of the Tachymetric Scale
With the advent of motorsports in the 20th century, the tachymetric scale began to take its place on the features of timepieces. Brands of luxury watches, such as TAG Heuer and Rolex, recognized its potential and enhanced its functionality by incorporating it within the design of their chronographs.
The “Rolex Oyster Perpetual Cosmograph Daytona”, for instance, is popularly known for its tachymetric scale engraved on the bezel. Its use is not confined to motorsports; aviators, astronauts, and even medical professionals also leverage the capabilities of the tachymetric scale.
For example, Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin, and Michael Collins, the Apollo 11 astronauts, used a watch equipped with a tachymeter during their historic moon landing mission.
Furthermore, some doctors and nurses use it to calculate a patient’s heart rate over a minute, demonstrating the incredible versatility of the tachymetric scale.
Understanding the Tachymetric Scale
A tachymetric scale essentially works on the principle of converting elapsed time (in seconds per unit) to speed (in units per hour). Calculations using a tachymeter are based on a straightforward mathematical concept: Rate equals Distance divided by Time.
While its operational method might sound complex, using the tachymetric scale is rather simple. Select a fixed distance (like a mile or a kilometer), then start the chronograph at the beginning of the distance.
Once the distance is covered, the second hand on the chronograph will point to the speed scale, indicating the average speed.
However, it is important to note that the accuracy of the measurement with a tachymetric scale relies on maintaining a consistent speed. Thus, if the speed varies significantly while covering the distance, the calculation might not accurately represent the average speed.
The tachymetric scale, a prevalent detail on many wristwatches, is more than just an adornment. It is an engaging tool with a plethora of practical utilities.
It exemplifies the harmonious marriage between aesthetic appeal and practical functionality often found on chronographs.
The In’s and Out’s of Tachymetric Scale
Located on the bezel of a chronograph watch, a tachymetric scale serves as a tool to compute speed based on travel time or even determine distance considering speed.
While initially, it may seem quite intricate, gaining a thorough understanding of the mechanics and principles underlying its operation reveals its simplicity.
How Does A Tachymetric Scale Work?
The tachymetric scale works on the simple mathematical principle of (3600 / elapsed time). The factor 3600 comes from the number of seconds in an hour.
To use the tachymeter, you need to start the chronograph or stopwatch at a starting marker and stop it at the next marker – that could be a mile or kilometer, depending upon the unit of measurement you are using.
For example, if you’re driving a car and it takes you 45 seconds to travel one mile, looking at the tachymeter you would see that you’re driving at approximately 80 miles per hour, based on the position of the second hand.
It’s that simple – the tachymetric scale shows you the speed directly and you don’t have to calculate anything.
Tachymetric Scale and Distance Calculation
The tachymetric scale can also measure distance. This functionality is driven by the mathematical equation speed = distance/time. This means if you’re aware of your speed and the amount of time you’ve been moving, you can easily calculate the distance traveled.
Limitations of the Tachymetric Scale
While tachymeters provide quick and straightforward measurements, they are not without their limitations. They typically work best for events that occur within a 60-second time frame due to the way they are designed.
Tachymeter scales are also limited to measuring speeds greater than 60 units per hour, as the tachymetric scale cannot measure speeds less than that. Lastly, these measurements are typically approximate and should not be used for precise calculations.
Tachymeter’s Historical Significance
The tachymeter has a rich history dating back to the first quarter of the 19th century when Nicole et Capt, renowned watchmakers in London, first used the tachymeter in pocket watches.
However, it was not until the 20th century with the advent of chronograph wristwatches that tachymeters became popular.
Tachymetric Scales in Everyday Life
Although most commonly associated with sports or racing events, there are practical everyday uses for a tachymetric scale.
For instance, it can estimate the expected time of arrival on a trip, measure walking or running pace, or even gauge the speed of a moving object – all relying on the simple relationship of speed, time, and distance.
Today, we take a closer look at the tachymetric scale, an impressive tool used for approximating speed and distance in real-time.
Despite not being completely accurate, the tachymetric scale excels in providing valuable estimations that prove highly beneficial in various applications.
So, whenever you encounter a tachymetric scale on a chronograph or watch, you’ll have a solid understanding of the useful insights it can deliver.
Using a Tachymetric Scale
Although a tachymetric scale might appear intimidating at first, its usage simplifies with understanding. Suppose you have a stopwatch or a wristwatch with a tachymeter.
By timing a vehicle crossing a premeasured distance of one mile or one kilometer, the tachymetric scale reveals the average speed of the vehicle or object moving.
Application in Sports
Visualize a track and field scenario where a tachymeter comes into direct application. The speed of a runner, or the speed at which they complete a race, becomes clear quickly with the use of a chronograph equipped with a tachymetric scale.
By timing the race and utilizing the tachymeter functions, one can estimate the speed and provide important data for performance analysis.
Role in the Aviation Industry
Pilots have been chief users of tachymeters since the dawn of aviation. Used for navigational computations, understanding speed, and time calculations, pilots rely on a tachymetric scale for flight efficiency.
A tachymeter allows them to make precise measurements and make timely decisions during flights.
Also, in aviation, the tachymeter assists in calculating the rate of ascent or descent, vital for maintaining safe flying protocols. Such information might help accurately predict arrival times, and change speed or altitude if needed.
Tachymetric Scale in Motor Vehicles
Inside motor vehicles, tachymeters represent an essential tool for monitoring speed. While most cars have an onboard speedometer, a tachymeter provides another method for evaluating speed based on time traveled over a premeasured distance.
It becomes an especially beneficial tool in a scenario where traditional speedometers fail, offering a backup method to keep track of speed.
The Science Behind the Tachymetric Scale
To better understand the tachymetric scale, it’s elucidating to explore the mathematical side of it. The scale is based on the simple mathematical principle of converting the time taken to travel a fixed distance into speed.
This conversion, expressed as a formula, becomes Speed = Distance/Time. The tachymeter automates the arithmetic for the user by presenting the conversion on the scale around the outside of the watch or chronograph.
Benefits of Using a Tachymetric Scale
While a tachymetric scale may seem antiquated in this digital age, it nevertheless offers inherent benefits. For one, it is a mechanical, non-electronic tool, and therefore immune to electronic failures. This quality makes it dependable in critical scenarios where electronic devices may fail.
Moreover, it exists as a valuable skill set to have, especially for those engaged in activities or professions involving speed and distance calculations.
Knowing how to utilize a tachymeter could be lifesaving, whether you are a pilot, a sports coach, or a regular motorist.
Choosing the Right Tachymetric Scale
Just like buying a timepiece, choosing the right tachymetric scale heavily depends on what you will use it for.
For instance, if you’re a pilot, racer, or sports training enthusiast, you may want to opt for an accurate and straightforward tachymetric scale to aid with your speed measurements.
On the other hand, if you’re more into aesthetics, you may hunt for a timepiece with a tachymetric scale that complements the watch’s overall design and your style.
It’s also important to decide whether you prefer a mechanical or a digital tachymetric scale. The mechanical ones give a classic vintage appeal and are seen as more luxurious, but digital models can offer more functionalities and might be easier to read and use.
Using the Tachymetric Scale Properly
There’s a common misconception that tachymetric scales are hard to use. However, once you understand the ins and outs, they can be quite simple. It’s crucial to understand that a tachymetric scale is essentially a conversion tool used to work out speed or distance.
When using your tachymetric scale, the stopwatch function on your watch will be your best friend. Start the stopwatch when you begin traveling a known distance and stop the stopwatch once that distance is completed.
The hand on the chronograph should then be pointing to your average speed on the tachymetric scale.
Maintenance and Care
Like any other watch component, a tachymetric scale requires proper care to ensure its longevity, efficiency, and accuracy. Here are a few tips:
- Avoid Excessive Exposure to Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can fade the numbers and lines on the tachymetric scale, rendering it ineffective over time.
- Prevent Contact with Chemicals: Certain chemicals can cause discoloration or even corrosion. It’s essential to keep your watch away from harsh chemicals or solvents.
- Regular Cleaning: Regular cleaning will help keep the tachymetric scale clear and readable. Use a soft cloth and lukewarm water and avoid the use of abrasive materials or intense scrubbing.
- Professional Service: If you notice discrepancies in calculations or readability decreases, it might be time for professional service. In addition, regular professional servicing can ensure that your tachymetric scale remains accurate and efficient over time.
Conclusion!
A tachymetric scale is more than just a stylish addition to your timepiece; it’s a practical tool that makes calculating distances or speeds straightforward and quick. Understanding its functions, making the right choice based on your needs, using it correctly, and maintaining it can help you leverage the full potential of this useful tool.
Being informed about the tachymetric scale opens up a world of precise measurements and understanding speed and distance in a unique way.
By getting to grips with the intricate workings, history, and utilization of the tachymetric scale, we are better equipped to harness its full potential in various spheres of life.
As we’ve learned, choosing the right one for your needs and using it correctly can further enhance your productivity and efficiency.
Therefore, the tachymetric scale is more than just a relic of the past – it’s a demonstration of the complex mosaic of human innovation and a testament to our relentless pursuit of accuracy and efficiency in all our endeavors. Learn more about the tachymetric scale a.k.a tachymeter.